Inspecting the spatial fit residuals¶
What you will learn
You will learn how to use the csresmap script to inspect the spatial fit residuals.
After having done a maximum likelihood fit it is good practice to inspect the fit residuals. You do this with the csresmap script that creates a residual sky map of the events from which the fitted model components were subtracted. You run the csresmap script as follows:
$ csresmap
Input event list, counts cube, or observation definition XML file [events.fits] cntcube.fits
Input model cube file (generated with ctmodel) [NONE]
Input exposure cube file [NONE] expcube.fits
Input PSF cube file [NONE] psfcube.fits
Input background cube file [NONE] bkgcube.fits
Input model definition XML file [$CTOOLS/share/models/crab.xml] crab_results.xml
Residual map computation algorithm (SUB|SUBDIV|SUBDIVSQRT|SIGNIFICANCE) [SIGNIFICANCE]
Output residual map file [resmap.fits]
Note
csresmap is a Python script while the other tools that you have
used so far are C++ binary executables. From the User perspective, Python
scripts and C++ binary executables behave the same way, but to distinguish
both all Python scripts names start with cs while all C++ binary
executables names start with ct.
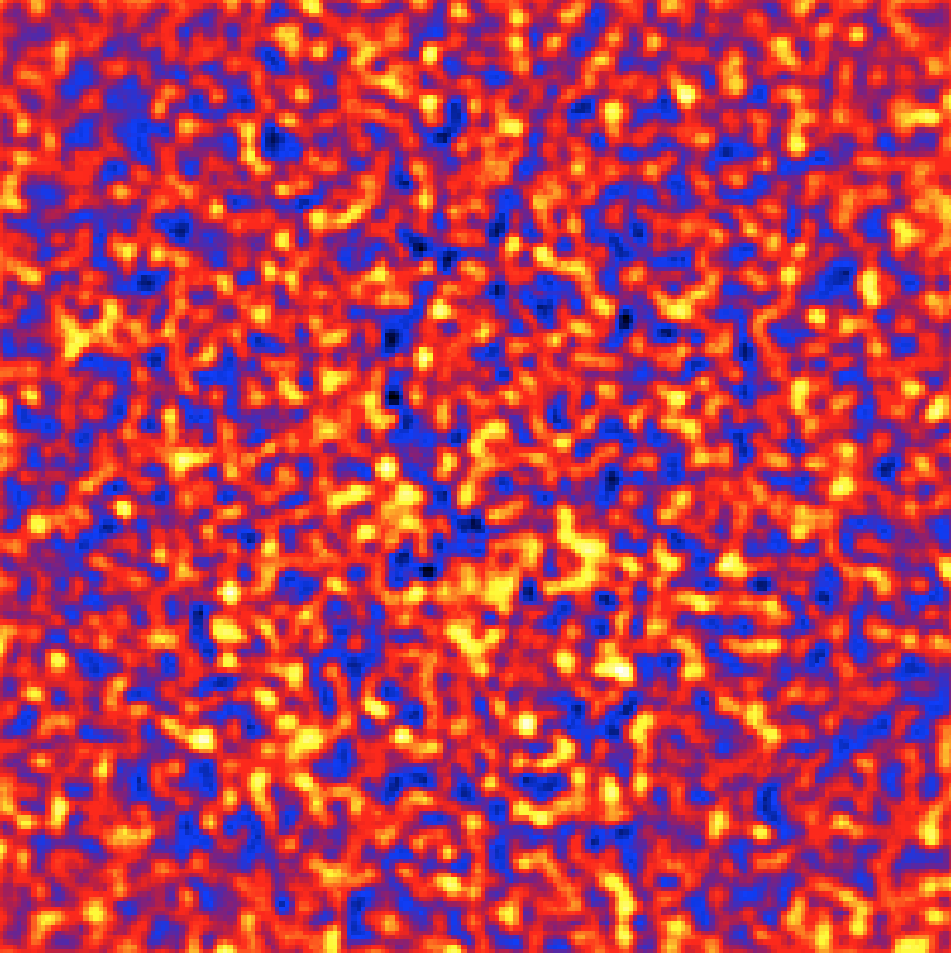
The csresmap script produces the FITS file resmap.fits that contains
the residual counts map. The image is displayed below using
ds9 with a linear color scale and with a 3 pixel Gaussian
kernel smoothing applied. Obviously, there are no significant residuals, which
indicates that the model fit was satisfactory.
Note
csresmap implements different algorithms for the computation of the residuals. These are:
SUB: \(DATA - MODEL\)SUBDIV: \((DATA - MODEL) / MODEL\)SUBDIVSQRT: \((DATA - MODEL) / \sqrt{MODEL}\)SIGNIFICANCE: \({\rm sign}(DATA-MODEL) \times \sqrt{ 2 \times ( DATA \times \ln \left(\frac{DATA}{MODEL} \right) + MODEL - DATA ) }\)
By default the SIGNIFICANCE algorithm is used.