Temporal components¶
Constant¶
The GModelTemporalConst class implements a temporal model that is constant in time and defined by
where the parameter in the XML definition has the following mapping:
\(N_0\) =
Normalization
The XML format for specifying a constant temporal model is:
<temporal type="Constant">
<parameter name="Normalization" scale="1.0" value="1.0" min="0.1" max="10.0" free="0"/>
</temporal>
Light Curve¶
The GModelTemporalLightCurve class implements a temporal model that defines an arbitrary light curve, defined by a function in a FITS file.
The only parameter of the model is a multiplicative normalization:
where the parameter in the XML definition has the following mapping:
\(N_0\) =
Normalization
The XML format for specifying a light curve is:
<temporal type="LightCurve" file="model_temporal_lightcurve.fits">
<parameter name="Normalization" scale="1" value="1.0" min="0.0" max="1000.0" free="0"/>
</temporal>
If the file attribute is a relative path, the path is relative to the
directory where the XML file resides. Alternatively, an absolute path may be
specified. Any environment variable present in the path name will be
expanded.
The structure of the light curve FITS file is shown in the figure below.
The light curve is defined in the first extension of the FITS file and
consists of a binary table with the columns TIME and NORM.
Times in the TIME columns are given in seconds and are counted with
respect to a time reference that is defined in the header of the binary
table. Times need to be specified in ascending order. The values in the
NORM column specify \(r(t)\) at times \(t\), and should be
comprised between 0 and 1.
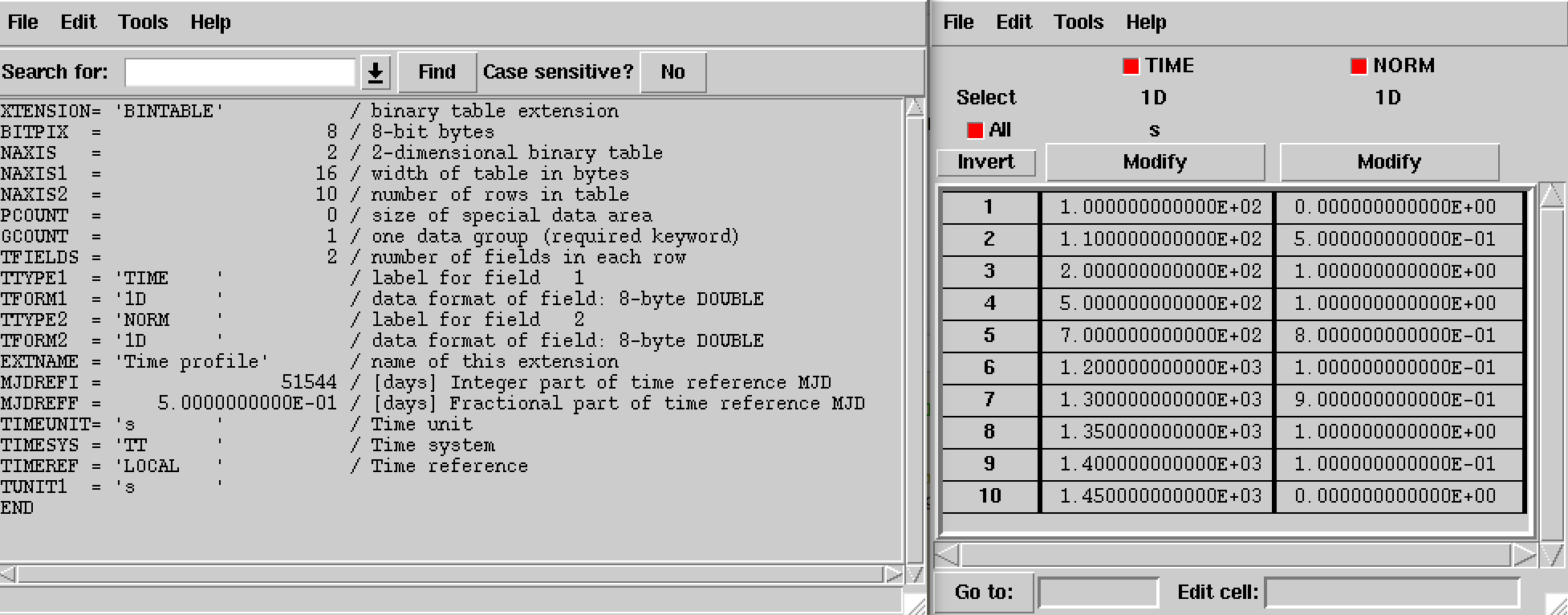
Structure of light curve FITS file¶
Phase Curve¶
The GModelTemporalPhaseCurve class implements a temporal model that defines a temporal variation based on an arbitrary phase \(\Phi(t)\) that is computed using
where
\(t_0\) is a reference time,
\(\Phi_0\) is the phase at the reference time,
\(f\) is the variation frequency at the reference time,
\(\dot{f}\) is the first derivative of the variation frequency at the reference time, and
\(\ddot{f}\) is the second derivative of the variation frequency at the reference time.
The temporal variation is computed using
The parameters in the XML definition have the following mappings:
\(N_0\) =
Normalization\(t_0\) =
MJD\(\Phi_0\) =
Phase\(f\) =
F0\(\dot{f}\) =
F1\(\ddot{f}\) =
F2
The XML format for specifying a phase curve is:
<temporal type="PhaseCurve" file="model_temporal_phasecurve.fits">
<parameter name="Normalization" scale="1" value="1.0" min="0.0" max="1000.0" free="0"/>
<parameter name="MJD" scale="1" value="51544.5" min="0.0" max="100000.0" free="0"/>
<parameter name="Phase" scale="1" value="0.0" min="0.0" max="1.0" free="0"/>
<parameter name="F0" scale="1" value="1.0" min="0.0" max="1000.0" free="0"/>
<parameter name="F1" scale="1" value="0.1" min="0.0" max="1000.0" free="0"/>
<parameter name="F2" scale="1" value="0.01" min="0.0" max="1000.0" free="0"/>
</temporal>
If the file attribute is a relative path, the path is relative to the
directory where the XML file resides. Alternatively, an absolute path may be
specified. Any environment variable present in the path name will be
expanded.
The structure of the phase curve FITS file is shown in the figure below.
The phase curve is defined in the first extension of the FITS file and
consists of a binary table with the columns PHASE and NORM.
Phase values in the PHASE column need to be comprised between 0 and 1
and need to be given in ascending order. The values in the NORM column
specify \(r(\Phi(t))\) at phases \(\Phi(t)\), and should be comprised
between 0 and 1.
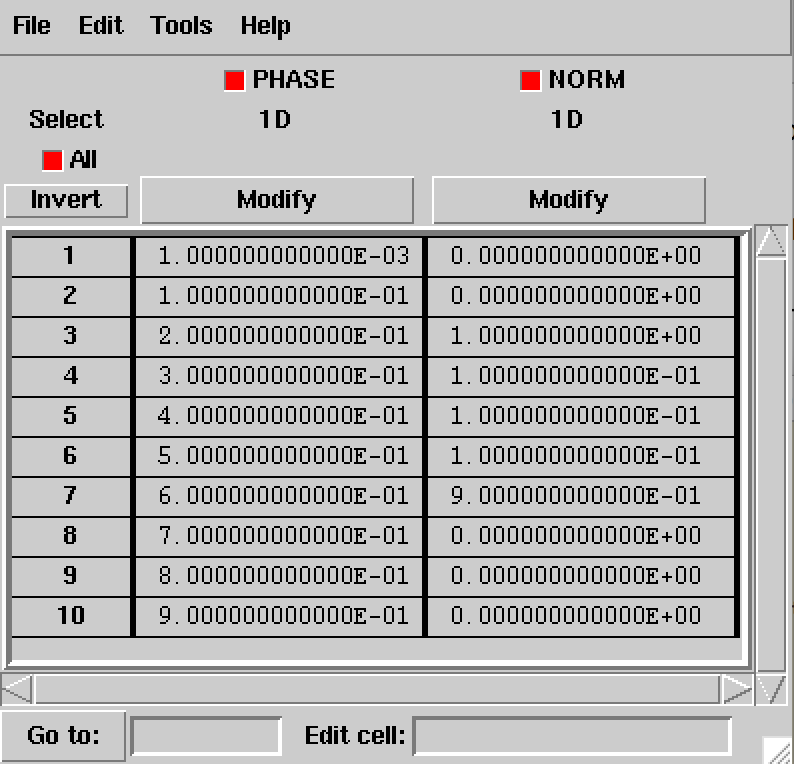
Structure of phase curve FITS file¶
By default, the NORM values are recomputed internally so that the
phase-averaged normalisation is one. In that case, the spectral component corresponds
to the phase-averaged spectrum. If the internal normalisation should be disabled
the normalize="0" attribute needs to be added to the temporal tag, i.e.
<temporal type="PhaseCurve" file="model_temporal_phasecurve.fits" normalize="0">
In that case the NORM values are directly multiplied with the spectral
component.
