Generating a sky map¶
What you will learn
You will learn how to use the ctskymap tool to generate a sky map from the selected event data.
Now let’s have a look into the selected data by generating a sky map. You do this with the ctskymap tool as follows:
$ ctskymap
Input event list or observation definition XML file [events.fits] selected_events.fits
Coordinate system (CEL - celestial, GAL - galactic) (CEL|GAL) [CEL]
Projection method (AIT|AZP|CAR|GLS|MER|MOL|SFL|SIN|STG|TAN) [CAR]
First coordinate of image center in degrees (RA or galactic l) (0-360) [83.63]
Second coordinate of image center in degrees (DEC or galactic b) (-90-90) [22.01]
Image scale (in degrees/pixel) [0.02]
Size of the X axis in pixels [200]
Size of the Y axis in pixels [200]
Lower energy limit (TeV) [0.1]
Upper energy limit (TeV) [100.0]
Background subtraction method (NONE|IRF|RING) [NONE]
Output skymap file [skymap.fits]
The tool produces the file skymap.fits which contains a sky map of the
events in FITS format. The sky map is centred on the location of the Crab
nebula (Right Ascension 83.63 deg, Declination 22.01 deg) and consists of
200 x 200 spatial pixels of 0.02 x 0.02 degrees in size, covering
an area of 4 deg x 4 deg.
Below an image of the sky map, displayed using ds9 in logarithmic color scale with a 3 pixel Gaussian kernel smoothing applied:

Sky map of the selected events¶
The sky map shows the Crab nebula on top of a wide-spread distribution of
events that originates from the instrumental background.
The
instrument response functions
contain templates that describe the spatial and spectral distribution of
the background, and ctskymap can make use of these templates
to subtract the background contribution from the sky map.
You enable the background subtraction by running the ctskymap tool with
the background subtraction method set to IRF, as shown in the following
example:
$ ctskymap
Input event list or observation definition XML file [selected_events.fits]
Coordinate system (CEL - celestial, GAL - galactic) (CEL|GAL) [CEL]
Projection method (AIT|AZP|CAR|GLS|MER|MOL|SFL|SIN|STG|TAN) [CAR]
First coordinate of image center in degrees (RA or galactic l) (0-360) [83.63]
Second coordinate of image center in degrees (DEC or galactic b) (-90-90) [22.01]
Image scale (in degrees/pixel) [0.02]
Size of the X axis in pixels [200]
Size of the Y axis in pixels [200]
Lower energy limit (TeV) [0.1]
Upper energy limit (TeV) [100.0]
Background subtraction method (NONE|IRF|RING) [NONE] IRF
Calibration database [prod2]
Instrument response function [South_0.5h]
Output skymap file [skymap.fits] skymap_subtracted.fits
The resulting sky map, displayed using ds9 in logarithmic color scale with a 3 pixel Gaussian kernel smoothing applied is shown below:
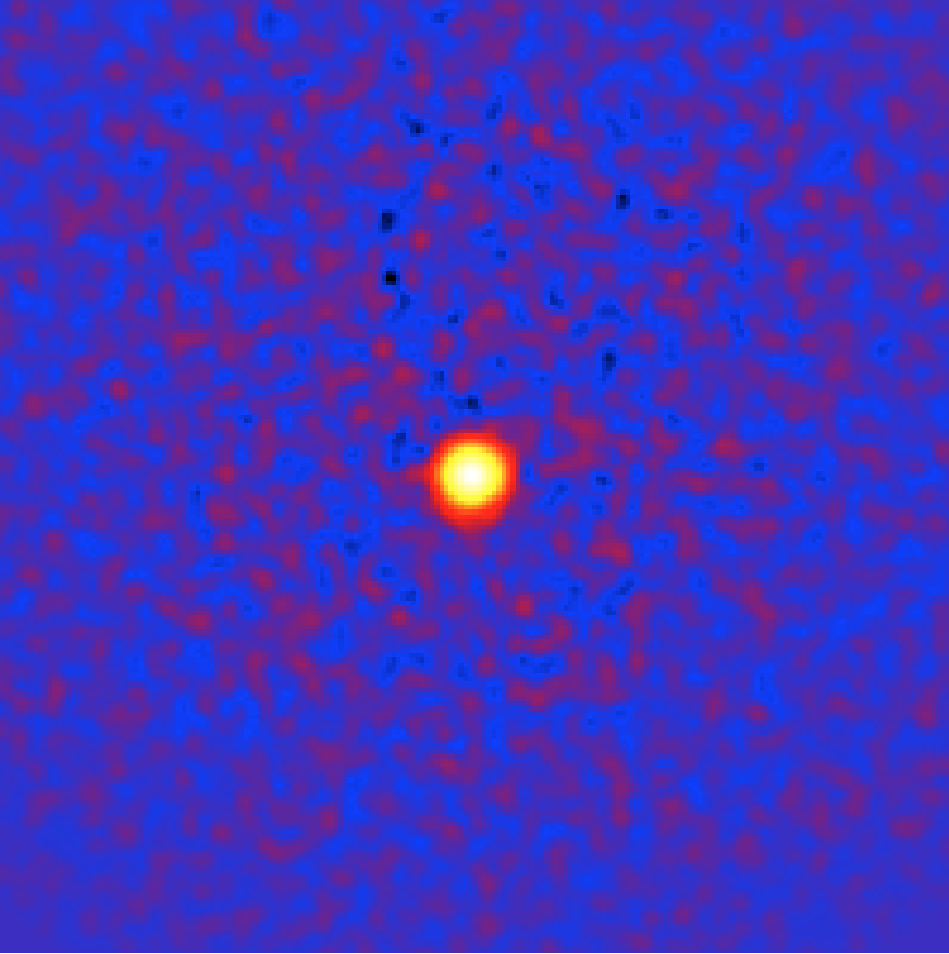
Sky map of the selected events with background subtraction from the IRFs¶
If a reliable model of the instrumental background is not available,
you can estimate it from the data by running the ctskymap tool with
the background subtraction method set to RING. For each position in
the map the number of background counts is estimated from a ring,
scaled according to the background model in the instrument
response functions, and subtracted from a circular
region centred on the trial source region. Regions with with significant
gamma-ray emission need to be excluded from the ring background estimate.
You can do this by iteratively determining an exclusion map that contains
all pixels above a given significance threshold. We chose here 3 iterations
and a threshold of 5 sigma.
$ ctskymap
Input event list or observation definition XML file [selected_events.fits]
Coordinate system (CEL - celestial, GAL - galactic) (CEL|GAL) [CEL]
Projection method (AIT|AZP|CAR|GLS|MER|MOL|SFL|SIN|STG|TAN) [CAR]
First coordinate of image center in degrees (RA or galactic l) (0-360) [83.63]
Second coordinate of image center in degrees (DEC or galactic b) (-90-90) [22.01]
Image scale (in degrees/pixel) [0.02]
Size of the X axis in pixels [200]
Size of the Y axis in pixels [200]
Lower energy limit (TeV) [0.1]
Upper energy limit (TeV) [100.0]
Background subtraction method (NONE|IRF|RING) [IRF] RING
Source region radius for estimating on-counts (degrees) [0.1] 0.05
Inner background ring radius (degrees) [0.6]
Outer background ring radius (degrees) [0.8]
Number of iterations for exclusion regions computation (0-100) [0] 3
Significance threshold for exclusion regions computation [5.0]
Calibration database [prod2]
Instrument response function [South_0.5h]
Output skymap file [skymap_subtracted.fits] skymap_ring.fits
The resulting sky map, displayed using ds9 in logarithmic color scale is shown below.
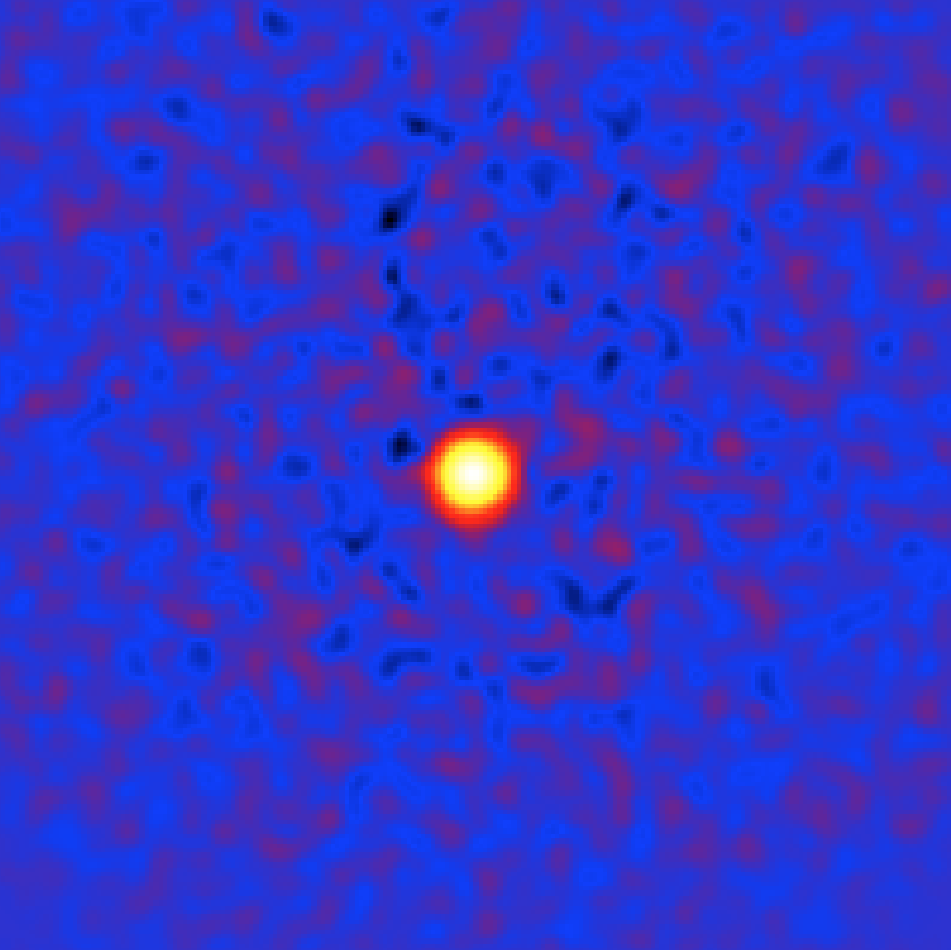
Sky map of the selected events with background subtraction from the ring method¶