How to generate a Test Statistic map?¶
What you will learn
You will learn how to generate a map of source detection significances to localise a gamma-ray source.
If you want to know how the Test Statistic changes with source position you can create a Test Statistic map using the cttsmap tool. A Test Statistic map is for example useful to study the precise error contours of the source location, or to search for significant sources in a field.
An example for a cttsmap run is shown below. The example is based on a stacked maximum likelihood analysis and generates a Test Statistic map of size 0.5 x 0.5 degrees, centred on the Galactic Centre.
$ cttsmap
Input event list, counts cube or observation definition XML file [events.fits] cntcube.fits
Input exposure cube file [NONE] expcube.fits
Input PSF cube file [NONE] psfcube.fits
Input background cube file [NONE] bkgcube.fits
Test source name [Crab] Test
Input model definition XML file [$CTOOLS/share/models/crab.xml] $CTOOLS/share/models/test_cube.xml
Coordinate system (CEL - celestial, GAL - galactic) (CEL|GAL) [CEL] GAL
Projection method (AIT|AZP|CAR|GLS|MER|MOL|SFL|SIN|STG|TAN) [CAR]
First coordinate of image center in degrees (RA or galactic l) (0-360) [83.63] 0.0
Second coordinate of image center in degrees (DEC or galactic b) (-90-90) [22.01] 0.0
Image scale (in degrees/pixel) [0.02] 0.05
Size of the X axis in pixels [200] 10
Size of the Y axis in pixels [200] 10
Output Test Statistic map file [tsmap.fits]
The cttsmap tool creates a FITS file containing for each pixel the Test Statistic value as well as the fit parameters for the test source. The figure below shows the resulting Test Statistic map.
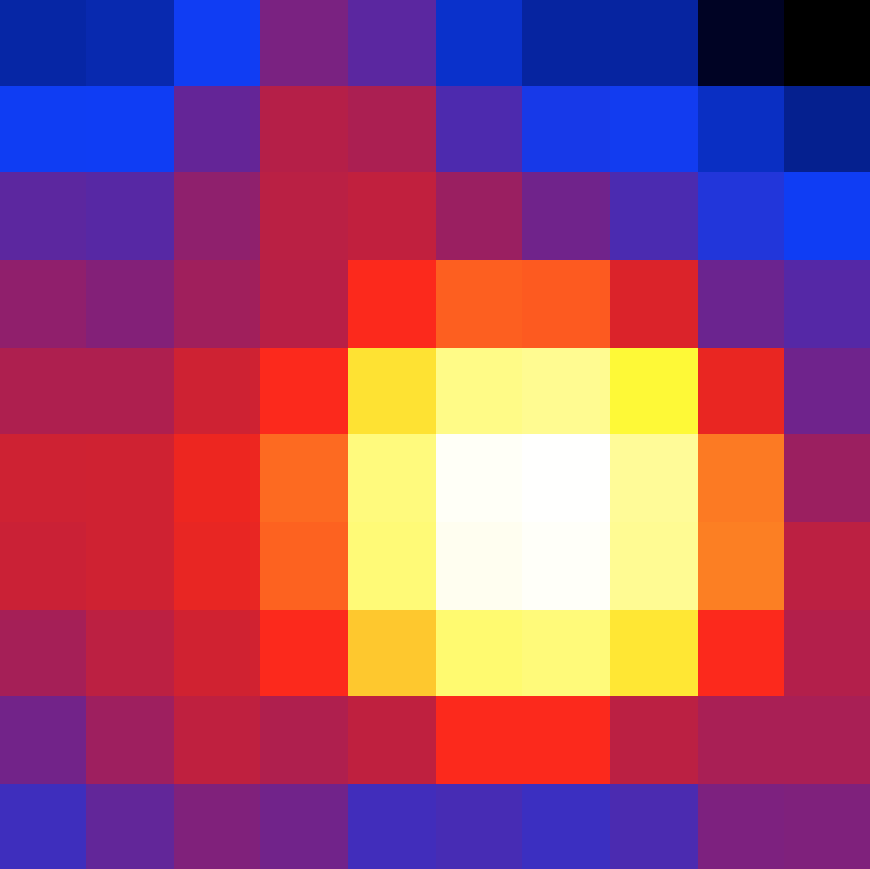
Test Statistic map around the Galactic centre¶
Note
The computation of a Test Statistic map is quite time consuming since a model
fit is done for each map position. The cttsmap tool will take one
of the sources in the
model definition file
(here Src001), displace the source to the bin centre of each map pixel,
and perform a maximum likelihood fit for this modified model to compute
the Test Statistic value.
The binmin and binmax parameters can be used to compute only a
subset of the bins in a map (see cttsmap). This functionality is
used by the cstsmapsplit script to generate a command sequence that is
useful for parallelizing the Test Statistic map computation. The
cstsmapmerge script can then be used to recombine the different
partial maps into a single Test Statistic map.
To produce the same result that was produced above by the single cttsmap run, now however split over ten cttsmap jobs that can be executed in parallel, type
$ cstsmapsplit
Input event list, counts cube or observation definition XML file [events.fits] cntcube.fits
Input exposure cube file [NONE] expcube.fits
Input PSF cube file [NONE] psfcube.fits
Input background cube file [NONE] bkgcube.fits
Input model definition XML file [$CTOOLS/share/models/crab.xml] $CTOOLS/share/models/test_cube.xml
Coordinate system (CEL - celestial, GAL - galactic) (CEL|GAL) [CEL] GAL
Projection method (AIT|AZP|CAR|GLS|MER|MOL|SFL|SIN|STG|TAN) [CAR]
First coordinate of image center in degrees (RA or galactic l) (0-360) [83.63] 0.0
Second coordinate of image center in degrees (DEC or galactic b) (-90-90) [22.01] 0.0
Image scale (in degrees/pixel) [0.02] 0.05
Size of the X axis in pixels [200] 10
Size of the Y axis in pixels [200] 10
Test source name [Crab] Test
Output Test Statistic map file [tsmap.fits] tsmap_split.fits
Number of TS map bins per task [5] 10
Compute null hypothesis first? [yes]
ASCII file containing all commands [commands.dat] tsmap_commands.dat
The cstsmapsplit script creates the following ASCII file on output:
cttsmap inobs=cntcube.fits inmodel=$CTOOLS/share/models/test_cube.xml srcname=Test expcube=expcube.fits psfcube=psfcube.fits bkgcube=bkgcube.fits nxpix=10 nypix=10 binsz=0.05 coordsys=GAL proj=CAR xref=0.0 yref=0.0 logL0=-447785.5939102234 binmin=0 binmax=10 outmap=tsmap_split_0.fits logfile=tsmap_split_0.log &
cttsmap inobs=cntcube.fits inmodel=$CTOOLS/share/models/test_cube.xml srcname=Test expcube=expcube.fits psfcube=psfcube.fits bkgcube=bkgcube.fits nxpix=10 nypix=10 binsz=0.05 coordsys=GAL proj=CAR xref=0.0 yref=0.0 logL0=-447785.5939102234 binmin=10 binmax=20 outmap=tsmap_split_1.fits logfile=tsmap_split_1.log &
cttsmap inobs=cntcube.fits inmodel=$CTOOLS/share/models/test_cube.xml srcname=Test expcube=expcube.fits psfcube=psfcube.fits bkgcube=bkgcube.fits nxpix=10 nypix=10 binsz=0.05 coordsys=GAL proj=CAR xref=0.0 yref=0.0 logL0=-447785.5939102234 binmin=20 binmax=30 outmap=tsmap_split_2.fits logfile=tsmap_split_2.log &
cttsmap inobs=cntcube.fits inmodel=$CTOOLS/share/models/test_cube.xml srcname=Test expcube=expcube.fits psfcube=psfcube.fits bkgcube=bkgcube.fits nxpix=10 nypix=10 binsz=0.05 coordsys=GAL proj=CAR xref=0.0 yref=0.0 logL0=-447785.5939102234 binmin=30 binmax=40 outmap=tsmap_split_3.fits logfile=tsmap_split_3.log &
cttsmap inobs=cntcube.fits inmodel=$CTOOLS/share/models/test_cube.xml srcname=Test expcube=expcube.fits psfcube=psfcube.fits bkgcube=bkgcube.fits nxpix=10 nypix=10 binsz=0.05 coordsys=GAL proj=CAR xref=0.0 yref=0.0 logL0=-447785.5939102234 binmin=40 binmax=50 outmap=tsmap_split_4.fits logfile=tsmap_split_4.log &
cttsmap inobs=cntcube.fits inmodel=$CTOOLS/share/models/test_cube.xml srcname=Test expcube=expcube.fits psfcube=psfcube.fits bkgcube=bkgcube.fits nxpix=10 nypix=10 binsz=0.05 coordsys=GAL proj=CAR xref=0.0 yref=0.0 logL0=-447785.5939102234 binmin=50 binmax=60 outmap=tsmap_split_5.fits logfile=tsmap_split_5.log &
cttsmap inobs=cntcube.fits inmodel=$CTOOLS/share/models/test_cube.xml srcname=Test expcube=expcube.fits psfcube=psfcube.fits bkgcube=bkgcube.fits nxpix=10 nypix=10 binsz=0.05 coordsys=GAL proj=CAR xref=0.0 yref=0.0 logL0=-447785.5939102234 binmin=60 binmax=70 outmap=tsmap_split_6.fits logfile=tsmap_split_6.log &
cttsmap inobs=cntcube.fits inmodel=$CTOOLS/share/models/test_cube.xml srcname=Test expcube=expcube.fits psfcube=psfcube.fits bkgcube=bkgcube.fits nxpix=10 nypix=10 binsz=0.05 coordsys=GAL proj=CAR xref=0.0 yref=0.0 logL0=-447785.5939102234 binmin=70 binmax=80 outmap=tsmap_split_7.fits logfile=tsmap_split_7.log &
cttsmap inobs=cntcube.fits inmodel=$CTOOLS/share/models/test_cube.xml srcname=Test expcube=expcube.fits psfcube=psfcube.fits bkgcube=bkgcube.fits nxpix=10 nypix=10 binsz=0.05 coordsys=GAL proj=CAR xref=0.0 yref=0.0 logL0=-447785.5939102234 binmin=80 binmax=90 outmap=tsmap_split_8.fits logfile=tsmap_split_8.log &
cttsmap inobs=cntcube.fits inmodel=$CTOOLS/share/models/test_cube.xml srcname=Test expcube=expcube.fits psfcube=psfcube.fits bkgcube=bkgcube.fits nxpix=10 nypix=10 binsz=0.05 coordsys=GAL proj=CAR xref=0.0 yref=0.0 logL0=-447785.5939102234 binmin=90 binmax=100 outmap=tsmap_split_9.fits logfile=tsmap_split_9.log &
wait
Now run the ASCII file by typing
$ ./tsmap_commands.dat
This will execute 10 cttsmap jobs in parallel. Each of the jobs will compute 10 pixels of the Test Statistic map. You combine the resulting 10 Test Statistic maps into a single map by typing
$ cstsmapmerge
Input TS map FITS files [tsmap.fits] tsmap_split_*.fits
Output TS map FITS file [NONE] tsmap_split.fits